Description
Key Technical Specifications (For Spare Part Verification)
- Part Number: PW301
- Output Voltage: +24 V DC (nominal)
- Output Current: Typically 5 A (verify label—some variants may differ)
- Input Voltage: 100–240 V AC, 50/60 Hz (universal input)
- Redundancy Support: Can be used in 1:1 redundant configuration with a second PW301 via optional redundancy module (e.g., RB301)
- Mounting: Plug-in module in standard Yokogawa I/O cabinet backplane (e.g., in AAI143, AAV144 racks)
- Indicators:
- POWER LED (green): Normal operation
- ALARM LED (red): Overload, overvoltage, or fan failure (if equipped)
- Protection Features:
- Overcurrent protection (OCP)
- Overvoltage protection (OVP)
- Short-circuit protection
- Thermal shutdown
- Cooling: Natural convection or forced air (depending on cabinet design)
- Certifications: CE, UL, CSA, and compliant with IEC 61326 (EMC for industrial environments)
-
YOKOGAWA PW301
System Role and Downtime Impact
The PW301 powers critical I/O subsystems in Yokogawa CENTUM CS 3000/VP systems widely deployed in oil & gas, chemical, power, and pharmaceutical plants. Each PW301 often supplies a full I/O card rack—supporting dozens of field signals.
Failure consequences include:
- Loss of all analog/digital I/O on the affected rack
- Disruption of regulatory control loops (e.g., flow, pressure, temperature)
- False alarms or missed trip conditions due to signal dropout
- Potential process unit shutdown if safety-critical measurements are lost
In non-redundant installations, a single PW301 failure can disable an entire process section. Even in redundant configurations, degraded power supply health increases risk during the second unit’s failure.
Reliability Analysis and Common Failure Modes
Despite robust industrial design, aging PW301 units are prone to:
- Electrolytic capacitor drying: Causes output ripple, voltage sag under load, or sudden shutdown
- Fan bearing wear (if fan-cooled): Leads to overheating and thermal shutdown
- Power semiconductor fatigue: MOSFETs or rectifiers degrade after years of thermal cycling
- Backplane connector corrosion: Especially in high-humidity environments
- Fuse degradation: Slow-blow fuses may fail open without visible signs
Preventive maintenance best practices:
- Monitor output voltage annually with a calibrated multimeter
- Inspect for bulging capacitors or burnt smell during cabinet access
- Verify redundancy switchover functionality during scheduled outages
Keep at least one tested spare per critical I/O cabinet
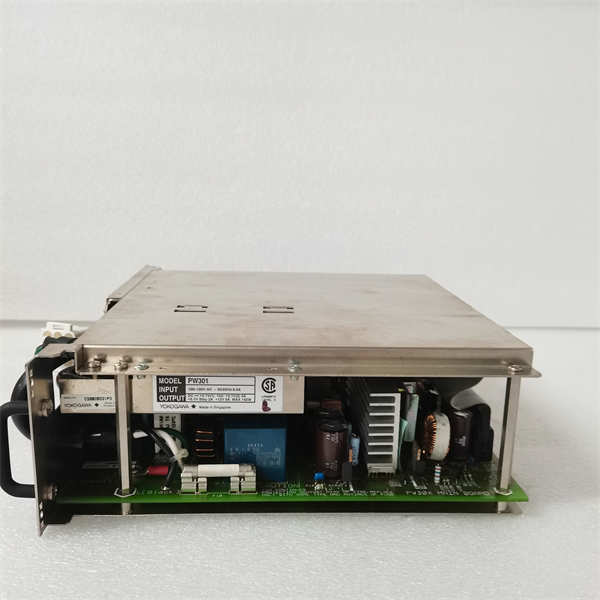

YOKOGAWA PW301
Lifecycle Status and Migration Strategy
Yokogawa has discontinued the PW301 in favor of higher-efficiency, higher-current successors:
- PW401: 8 A output, improved efficiency
- PW402: Dual-output variant
- PW501: For CENTUM VP R6+ systems, supports enhanced diagnostics
While Yokogawa still offers limited support for CS 3000 systems, new PW301 units are no longer manufactured.
Short-term mitigation:
- Source refurbished or NOS units through Yokogawa-authorized service partners
- Confirm compatibility with your cabinet backplane and fuse ratings
- Test spares under load before storage
Long-term strategic path:
Migrate to CENTUM VP R6/R7 or Yokogawa OpreX Control Platform, which offer:
- Higher power density and efficiency
- Built-in power monitoring and predictive diagnostics
- Cybersecurity compliance (IEC 62443)
- Extended lifecycle support
Migration involves:
- Replacing I/O cabinets or retrofitting with new power rails
- Updating engineering configuration in Integrated Production Management Suite
- Recommissioning I/O and control logic


 Tel:
Tel:  Email:
Email:  WhatsApp:
WhatsApp: 



