Description
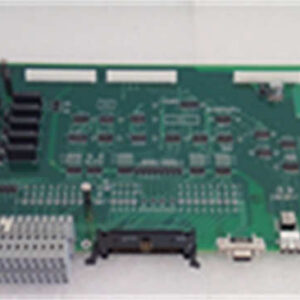
Technical Specifications (For Spare Parts Verification)
- Product Model: JANCD-XCP0101C-1
- Manufacturer: YASKAWA Electric Corporation
- System Compatibility: MOTOMAN XRC, NX, or early DX-series robot controllers
- Form Factor: Plug-in PCB card with edge connector
- Primary Function: Communication interface (likely RS-232/422 or DeviceNet/Profibus option)
- Connector Type: Onboard headers or rear-panel D-sub (varies by configuration)
- Firmware: Masked ROM or EPROM-based; non-upgradable
- Power Supply: +5 VDC and ±12 VDC from backplane
- Mounting: Secured within controller chassis via guide rails and screws
- Diagnostic Indicators: May include status LEDs for TX/RX activity
- Revision Marking: “C-1” suffix indicates hardware/firmware revision; must match host system requirements
System Role and Downtime Impact
The JANCD-XCP0101C-1 is installed inside the main cabinet of legacy Yaskawa robot controllers, acting as the primary bridge between the robot’s internal motion logic and the factory automation network. It enables critical functions such as cycle start/stop signaling, position reporting, fault handshaking, and program selection from a PLC. In an automotive spot-welding cell, for example, loss of this card would prevent the robot from receiving “go” signals from the line PLC, halting the entire station. Because these older controllers lack redundant communication paths, this single board represents a single point of failure with direct impact on Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE).
Reliability Analysis and Common Failure Modes
After 15–25 years of continuous operation, the JANCD-XCP0101C-1 is vulnerable to several age-related failure mechanisms:
- EPROM data corruption: UV-erasable or OTP memory chips degrade over time, leading to boot failures or erratic communication behavior.
- Serial transceiver IC failure: RS-422/485 driver chips (e.g., MAX488, SN75176) fail due to ground potential differences or ESD events, causing open or shorted communication lines.
- Solder joint fatigue: Thermal cycling induces micro-cracks around high-pin-count connectors or power regulation components.
- Capacitor aging: Onboard tantalum or electrolytic capacitors lose capacitance or develop high ESR, destabilizing local power rails and causing intermittent resets.
A key design limitation is the absence of galvanic isolation on many variants, making the card susceptible to ground loops in modern multi-vendor plants. Additionally, firmware is typically fixed—errors cannot be patched, and configuration is often stored in volatile RAM backed by a separate battery (which may also be depleted).
Preventive maintenance should focus on:
- Verifying communication signal integrity with an oscilloscope during routine cell checks.
- Inspecting the PCB for capacitor bulging, trace discoloration, or corrosion near connectors.
- Ensuring proper grounding between robot controller and PLC cabinet to minimize common-mode noise.
- Maintaining at least one verified spare unit powered periodically to prevent storage-related degradation.
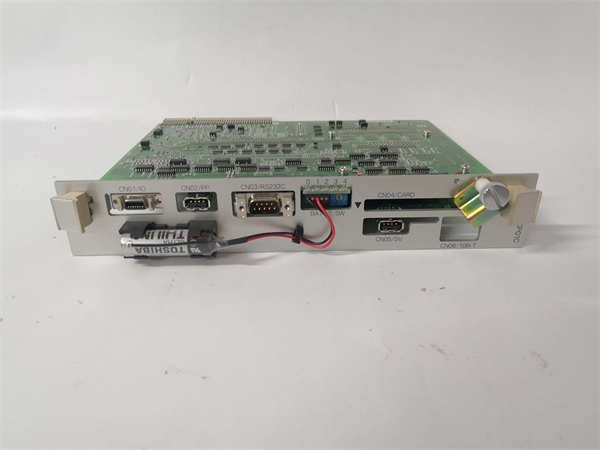

YASKAWA JANCD-XCP0101C-1
Lifecycle Status and Migration Strategy
Yaskawa has discontinued the JANCD-XCP0101C-1 and no longer provides repair services or technical documentation for this legacy card. Continuing to operate systems dependent on it exposes facilities to escalating risk: diminishing spare quality, inability to recover from configuration loss, and lack of engineering expertise.
As a temporary measure:
- Source and functionally test multiple spares from reputable industrial surplus vendors.
- Document pinout, baud rate, and protocol settings (e.g., Modbus RTU, Yaskawa-specific ASCII) for rapid recovery.
- Consider external protocol converters (e.g., Anybus Serial-to-EtherNet/IP) to offload communication burden if the native port is unstable.
For long-term sustainability, Yaskawa’s official migration path is upgrading to the YRC1000 or DX200 controller platform. This involves:
- Replacing the entire robot controller cabinet
- Revalidating robot programs and I/O mappings
- Integrating via modern standards like EtherNet/IP, PROFINET, or OPC UA
While capital-intensive, this upgrade eliminates dependency on obsolete hardware, improves cybersecurity posture, and aligns robotic cells with current Industry 4.0 connectivity expectations. For cells with extended operational life plans beyond 2027, migration is strongly recommended.



 Tel:
Tel:  Email:
Email:  WhatsApp:
WhatsApp: