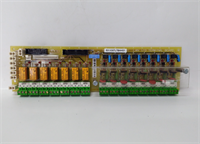
Description
Key Technical Specifications (For Spare Part Verification)
- Product Model: MRP768176 / IS200TDBTH6ABC
- Manufacturer: GE Power (designed for Mark VIe platform; manufactured under contract by third-party electronics suppliers)
- System Family: GE Mark VIe distributed control system (specifically for TDBT-type I/O packs)
- Module Type: Terminal Base Board (TBB) — passive but functionally critical interface layer
- Compatible I/O Cards: Designed to mate with IS200TVIBH (vibration), IS200TBAIH (analog input), or similar H-series I/O modules
- Field Connections: Screw-terminal blocks for up to 16 analog signals (depending on paired I/O card)
- Signal Conditioning: Includes filtering, transient suppression, and optional isolation components (varies by revision)
- Mechanical Interface: Snap-in design for Mark VIe I/O carrier chassis; keyed to prevent misinsertion
- Revision Sensitivity: “H6ABC” suffix indicates specific hardware/firmware compatibility; not all TDBTH revisions are interchangeable
- Operating Environment: Rated for industrial control enclosures (0°C to +60°C, non-condensing)
System Role and Downtime Impact
The IS200TDBTH6ABC is not a “smart” module—it contains no processors—but it is indispensable. It serves as the bridge between the rugged field wiring of a power plant and the sensitive electronics of the Mark VIe I/O cards. Each terminal board is custom-configured for its paired I/O module type, with trace-level jumpers, filter networks, and surge protection tailored to signal types (e.g., mV thermocouples vs. 4–20 mA pressure transmitters).
If this board fails—due to terminal corrosion, cracked solder joints, or damaged transient suppressors—the corresponding I/O channels become unreliable or dead. In a triple-modular redundant (TMR) Mark VIe system, loss of one channel may degrade voting logic; in simplex auxiliary systems, it can cause nuisance trips or blind operation. Replacement requires matching not just the part number, but the exact revision (“H6ABC”), as earlier or later versions may have different grounding schemes or filter characteristics that affect system stability.
Reliability Analysis and Common Failure Modes
As a passive electromechanical component, the IS200TDBTH6ABC is generally robust—but decades of thermal cycling, vibration, and environmental exposure take a toll:
- Terminal block degradation: Repeated tightening/loosening or thermal expansion causes plastic fatigue, leading to loose connections and intermittent signals.
- Solder joint cracking: Especially around high-mass components or edge connectors, exacerbated by turbine hall vibration.
- Surge suppressor failure: MOVs or TVS diodes degrade after repeated voltage spikes, eventually shorting or opening, which can distort analog signals.
- Revision mismatch errors: Installing a non-matching TDBTH (e.g., H5 vs. H6) may appear physically compatible but introduce grounding loops or bandwidth limitations, causing noise or drift.
Recommended maintenance practices:
- Perform annual torque checks on terminal screws using calibrated tools (per GE specs).
- Inspect for discoloration, arcing marks, or white powder (corrosion) on terminals and PCB traces.
- Verify continuity and isolation resistance during outages using a megohmmeter.
- Store spares in dry, static-controlled environments; avoid handling by edge fingers to prevent ESD damage.
MRP768176 IS200TDBTH6ABC GE
Lifecycle Status and Migration Strategy
GE has discontinued the IS200TDBTH series as part of the broader transition from Mark VIe to Mark VIe+. No new units are manufactured, and official support is limited to existing service contracts. The secondary market is fragmented, with many sellers unable to confirm revision compatibility or prior usage history.
Short-term actions:
- Audit existing inventory to confirm revision codes match installed base.
- Source only from vendors who provide photos, continuity test reports, and revision verification.
- Consider keeping one spare per I/O pack type per turbine, even if currently functional.
Long-term path: GE’s strategic direction is migration to Mark VIe+, which uses integrated I/O modules with built-in terminations (eliminating separate TBBs). This reduces parts count and improves diagnostics but requires full I/O chassis replacement and re-commissioning. For plants extending life beyond 2030, initiating a phased migration study is advisable. Until then, disciplined spare management and preventive inspection remain the only defenses against unplanned downtime caused by this deceptively simple—but mission-critical—component.

 Tel:
Tel:  Email:
Email:  WhatsApp:
WhatsApp: