Description
Key Technical Specifications (For Spare Part Verification)
- Product Model: 81001-450-53-R
- Manufacturer: Mitsubishi Electric
- System Family: MELSEC A1S PLC platform
- Output Voltage: +5V DC (for backplane logic), +24V DC (for I/O and sensors)
- Rated Current: 5A on +5V line (hence “53” designation)
- Input Voltage: 100–240V AC (auto-ranging)
- Mounting Type: Slot 0 in A1S base units (rack-mounted, occupies one module position)
- Dimensions: Standard A1S module width (approx. 42 mm)
- Cooling Method: Convection (no fan)
- Status Indicators: Power ON LED, fuse status (if equipped)
System Role and Downtime Impact
The 81001-450-53-R is the primary power supply unit installed in slot 0 of a MELSEC A1S modular PLC rack. It delivers stable low-voltage DC power to all modules in the chassis, including the CPU, digital/analog I/O, and communication interfaces. In many legacy installations—particularly in automotive assembly, packaging lines, or water treatment plants—this module remains in service due to the longevity of the overall control system. Failure of this power supply results in immediate and complete loss of control: the CPU halts, outputs de-energize, and the entire automated process stops. Because the A1S architecture does not support redundant power supplies, there is no automatic failover. Consequently, unplanned failure of this obsolete module can lead to extended production downtime, especially if a verified spare is not already on hand.
Reliability Analysis and Common Failure Modes
Despite its solid-state design, the 81001-450-53-R is susceptible to age-related degradation common in power electronics from the 1990s–2000s era. The most frequent failure causes include drying out or bulging of electrolytic capacitors in the primary and secondary filtering stages, leading to output voltage ripple, instability, or complete shutdown. Over time, thermal cycling also fatigues solder joints—particularly around high-current components—causing intermittent connections. Another vulnerability is the input varistor or surge protection circuit, which can degrade after repeated exposure to line transients, eventually shorting and blowing the internal fuse. The module lacks active cooling, so operation in high-ambient-temperature cabinets accelerates component aging. For preventive maintenance, technicians should monitor the +5V and +24V rails with a multimeter during routine checks, inspect for capacitor leakage or bulging, ensure cabinet ventilation is unobstructed, and verify that input voltage remains within nominal range to reduce stress on aging components.
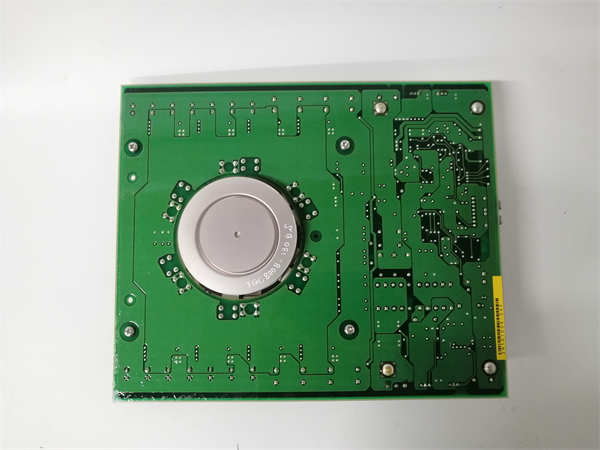

MITSUBISHI 81001-450-53-R
Lifecycle Status and Migration Strategy
Mitsubishi Electric has officially discontinued the A1S series, including the 81001-450-53-R power module, and no direct replacement exists in current product lines. Continued use carries significant operational risk: authentic spares are extremely scarce, and used units may have hidden wear. Official technical support is limited to existing service contracts, with no firmware or hardware updates available. As a short-term mitigation, facilities can maintain a stock of tested spares sourced from certified industrial surplus vendors or implement external redundant power schemes using DIN-rail mounted third-party PSUs (though this requires custom wiring and bypasses the original backplane power distribution). The recommended long-term solution is migration to the MELSEC iQ-R or Q Series platforms. This involves replacing the entire rack, CPU, I/O modules, and power supply—typically using the Q61P or R8P power units as modern equivalents. While this demands re-engineering and reprogramming (in GX Works3), it restores access to vendor support, improves energy efficiency, enhances diagnostic capabilities, and future-proofs the control system against further obsolescence.
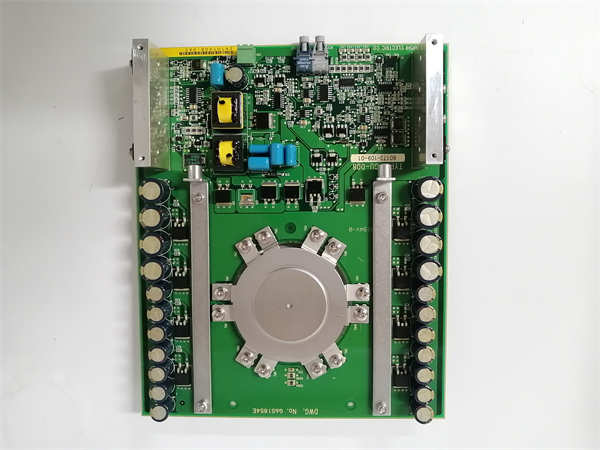


 Tel:
Tel:  Email:
Email:  WhatsApp:
WhatsApp: 



