Description
Technical Specifications (For Spare Part Verification)
- Product Model: TK-FPDXX2
- Manufacturer: HONEYWELL
- System Platform: Fail Safe Controller (FSC) – part of the Experion® Safety Manager legacy line
- Module Type: Redundant digital input module (1oo2 or 2oo2 architecture, depending on configuration)
- Input Channels: 16 channels, electrically isolated, suitable for dry contact or powered signals (typically 24 V DC)
- Input Voltage Range: 18 to 30 V DC (nominal 24 V DC)
- Diagnostic Coverage: Continuous wire-break and short-circuit monitoring per IEC 61508 requirements
- Redundancy Support: Dual independent signal paths with internal cross-comparison
- Backplane Interface: Proprietary FSC high-integrity safety bus
- SIL Certification: Certified for use in SIL 3 safety functions per IEC 61508 (TÜV-certified)
- Physical Form: Standard FSC rack-mounted card, front-panel LEDs for channel status, module OK, and fault indication
System Role and Downtime Impact
The TK-FPDXX2 is a foundational safety I/O module within Honeywell’s FSC (Fail Safe Controller) platform, widely deployed in refineries, chemical plants, LNG terminals, and power facilities. It resides in redundant controller chassis and is responsible for capturing critical binary field signals—such as valve position confirmations, pump run status, or emergency pushbuttons—and delivering them to the FSC logic solver with guaranteed diagnostic coverage and fault tolerance.
In a properly configured 1oo2 (one-out-of-two) or 2oo2 (two-out-of-two) architecture, the module ensures that a single hardware fault does not result in a dangerous undetected failure. However, if the TK-FPDXX2 fails completely or loses internal synchronization between its dual channels, the FSC system will typically initiate a safe state—triggering a full plant or unit shutdown. In non-redundant legacy installations, a faulty module may cause either nuisance trips or, more critically, fail to detect a real hazardous condition, violating the core purpose of the Safety Instrumented System (SIS). Given its role in life-safety and environmental protection, unavailability of this module directly impacts regulatory compliance and operational license.
Reliability Analysis and Common Failure Modes
Despite its robust design for safety-critical service, the TK-FPDXX2 is susceptible to age-related degradation common in industrial electronics from the late 1990s to early 2000s. The most prevalent failure mode involves optocoupler aging in the input isolation circuits. Over time, these components can exhibit increased propagation delay or reduced current transfer ratio, leading to missed signal transitions or false diagnostics.
Another vulnerability lies in the electrolytic capacitors on the internal power regulation stage. After 15+ years of continuous operation, these capacitors often dry out, causing voltage instability under load—especially during high ambient temperatures. This can manifest as intermittent module resets or “channel mismatch” faults.
The module is also sensitive to power supply quality. Voltage transients or ground loops—common in older plants—can damage the input protection circuitry or desynchronize redundant channels. Additionally, corrosion on backplane connectors due to humidity or hydrogen sulfide exposure can lead to communication errors with the FSC processor.
Recommended maintenance practices include: performing annual proof tests with simulated field signals to verify both channels respond identically; reviewing FSC event logs for “DIAG FAULT”, “INPUT ERROR”, or “SYNC LOSS” entries; and ensuring cabinet environmental conditions remain within specification (temperature <50°C, humidity <80% RH non-condensing). Any spare module must be functionally tested on a known-good FSC test rack before being placed into standby inventory.
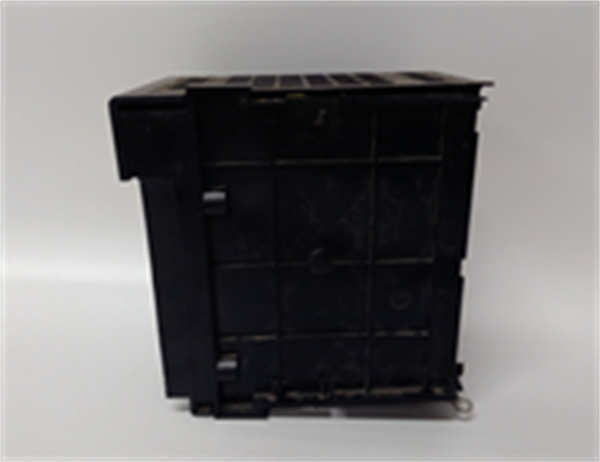

TK-FPDXX2 HONEYWELL
Lifecycle Status and Migration Strategy
Honeywell has officially discontinued the TK-FPDXX2 as part of the end-of-life (EOL) process for the legacy FSC platform. The company no longer manufactures this module, and technical support is restricted to customers with active maintenance agreements. Continuing to operate systems dependent on this component carries substantial risk: authentic spares are extremely scarce, prices have escalated, and counterfeit units have entered the gray market.
Short-term mitigation includes conducting a full inventory audit and securing only tested, traceable spares from certified suppliers. Some organizations pursue board-level repair, but this voids functional safety certification unless followed by full re-validation per IEC 61508—a costly and complex process requiring TÜV oversight.
The strategic migration path is to transition to Honeywell’s current Experion® Safety Manager platform (based on the SM series controllers). This modern SIS offers native support for advanced I/O modules with enhanced diagnostics, cybersecurity features (IEC 62443 compliant), and seamless integration with Experion PKS. While the migration requires re-engineering the safety application using Safety Builder software and re-validating all safety functions, it restores access to full vendor support, firmware updates, and long-term spare availability. Honeywell provides migration services, including factory acceptance testing (FAT) and site cutover planning, to minimize operational disruption. For facilities with extended operational mandates, this upgrade is essential to maintain safety integrity, regulatory standing, and insurance compliance.



 Tel:
Tel:  Email:
Email:  WhatsApp:
WhatsApp: