Description
Key Technical Specifications (For Spare Part Verification)
- Product Model: SR489-P1-HI-A20-E
- Manufacturer: GE Multilin (General Electric)
- Product Family: SR489 Motor Management Relay
- Protection Features:
- Thermal overload (IEC/ANSI curves)
- Phase unbalance, phase loss, reverse phase
- Stall/jam protection
- Ground fault (residual or core-balance CT input)
- High-Impedance Differential (HI) for internal winding fault detection
- Current Inputs: 3-phase + ground (5 A or 1 A CT compatible); HI inputs require auxiliary CTs
- Voltage Inputs: 3-phase VT (optional for power metering and undervoltage protection)
- Outputs: 6 programmable Form-C output contacts (trip, alarm, control)
- Communication: RS485 (Modbus RTU), front-panel IRIG-B for time sync (E suffix = enhanced comms)
- Power Supply: Universal 24–240 V AC/DC
- Mounting: Flush or panel mount (4.75″ x 7.5″ cutout)
- Standards Compliance: ANSI C37.96, IEC 60255
- Firmware Revision: Must match existing system configuration; non-upgradable without original software
System Role and Downtime Impact
The SR489-P1-HI-A20-E is deployed to protect medium- to large-voltage induction or synchronous motors (e.g., in pumps, compressors, or fans) in power plants, refineries, and industrial facilities. Its high-impedance differential (HI) function provides sensitive detection of internal stator winding faults—offering faster and more secure protection than traditional overcurrent methods. A relay failure or misoperation can result in either nuisance tripping (causing unnecessary downtime) or, worse, failure to trip during a fault—leading to catastrophic motor burnout, fire hazard, or cascading grid disturbances. In continuous-process industries, loss of a critical motor can halt production lines for days, with cost impacts exceeding $ 100,000 per hour.
Reliability Analysis and Common Failure Modes
Although designed for harsh environments, the SR489 is vulnerable to component aging after 10–15 years of service. The most prevalent issues include:
- Capacitor degradation on the power supply board, causing brownouts or reboot loops
- Relay contact welding on output modules due to frequent switching or inductive kickback
- CT input circuit drift, leading to inaccurate current measurement and false trips
- Communication port failure (RS485 transceiver damage from ground potential rise)
- Display or keypad malfunction due to membrane wear or moisture ingress
Environmental stressors like high ambient temperature (>50°C), dust, and electrical noise accelerate these failures. Recommended preventive actions include annual calibration checks using a secondary injection test set, visual inspection for bulging capacitors or burnt traces, verification of CT wiring integrity, and ensuring proper grounding of the relay chassis and shield wires.
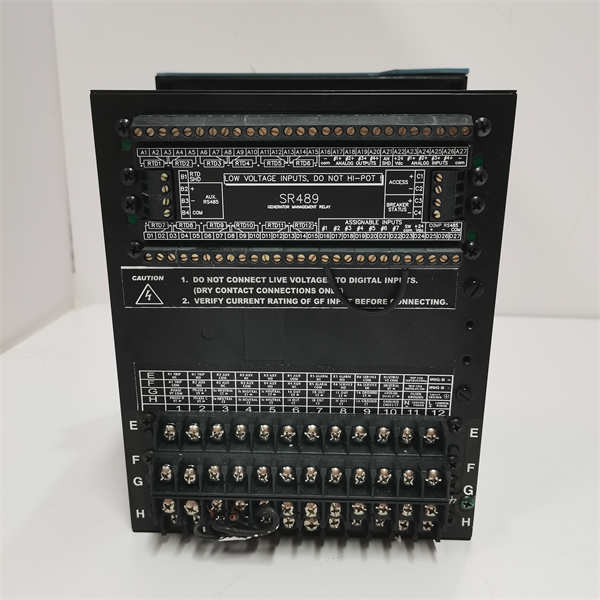

GE SR489-P1-HI-A20-E
Lifecycle Status and Migration Strategy
GE has officially discontinued the SR489 series, replacing it with the Multilin™ 489 (a rebranded but functionally similar unit) and, more strategically, the Multilin 889—a modern IEC 61850-compliant motor protection relay with Ethernet, waveform capture, and predictive diagnostics. However, the SR489-P1-HI-A20-E is no longer manufactured, and GE no longer provides repair services, firmware updates, or technical documentation for this specific configuration.
Short-term mitigation includes:
- Stocking tested spares with verified HI functionality
- Engaging third-party relay shops for board-level repairs (with caution on calibration validity)
Long-term, migration to the Multilin 889 is strongly recommended. This upgrade requires:
- Replacing CT/VT wiring if burden or accuracy class is incompatible
- Re-engineering protection logic in Enervista 889 software
- Updating SCADA integration (from Modbus RTU to IEC 61850 GOOSE/MMS or Modbus TCP)
While requiring capital investment, this transition eliminates obsolescence risk, enhances cybersecurity, enables remote diagnostics, and aligns with modern asset management strategies—ultimately improving plant safety and operational resilience.



 Tel:
Tel:  Email:
Email:  WhatsApp:
WhatsApp: