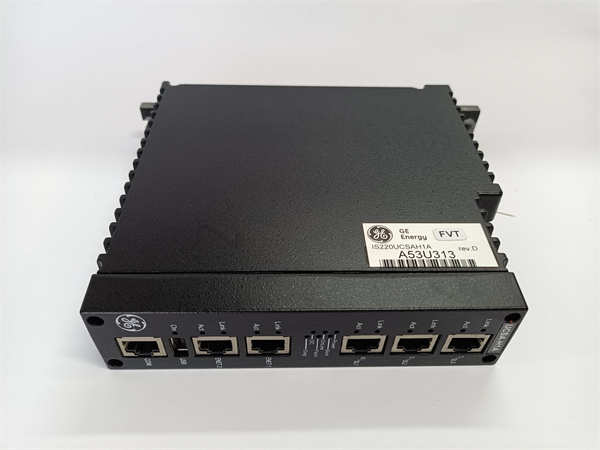
Description
Key Technical Specifications (For Spare Parts Verification)
- Product Model: IS220UCSAH1A
- Manufacturer: GE Power (formerly GE Energy)
- System Platform: Mark VIe Integrated Control System (ICS) for gas/steam turbines
- Form Factor: DIN-rail mounted I/O module for Mark VIe I/O Pack
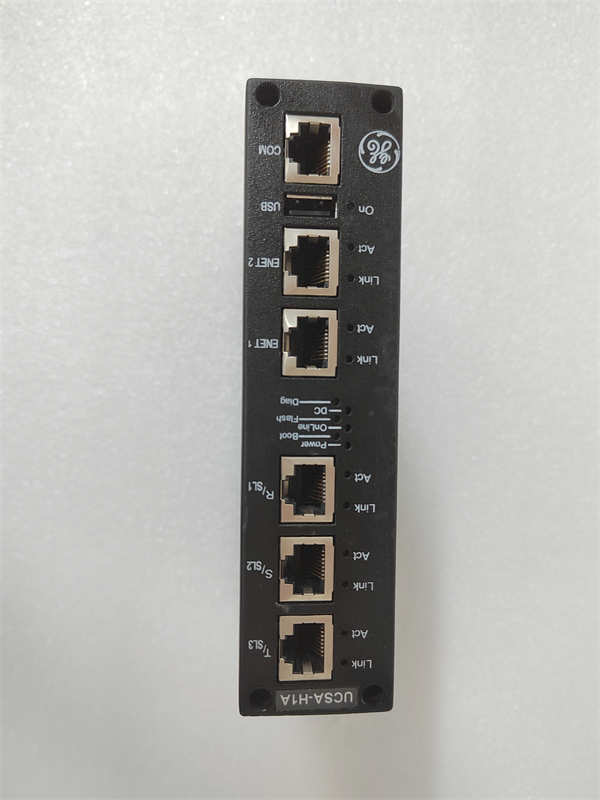
- Communication Interface: Dual 10/100 Mbps Ethernet ports (RJ-45)
- Protocol Support: Modbus TCP, GE’s proprietary EGD (Ethernet Global Data), and secure shell (SSH)
- Power Requirement: +24 V DC supplied via Mark VIe backplane
- Operating Temperature: 0°C to 60°C
- Firmware Dependency: Requires specific Mark VIe controller firmware version (typically v3.x or later)
- Physical Identifier: Label includes “IS220UCSAH1A” and unique serial number; revision code critical for compatibility
System Role and Downtime Impact
The IS220UCSAH1A serves as the primary network gateway in the GE Mark VIe architecture, bridging the safety-critical turbine control layer with the plant information layer. It is not part of the real-time control loop but is essential for operational visibility. If this module fails or becomes unresponsive, operators lose access to real-time trending, alarm history, and remote configuration capabilities. While the turbine may continue running in local mode, any event requiring off-site engineering support or regulatory data reporting will be severely hampered. In combined-cycle or peaking plants with remote operations centers, loss of UCSA functionality can effectively force a controlled shutdown for troubleshooting, leading to significant revenue loss.
Reliability Analysis and Common Failure Modes
Despite its obsolescence, many IS220UCSAH1A modules remain in service due to the long asset life of power generation equipment. However, age-related degradation is a growing concern. The most frequent failure modes include electrolytic capacitor drying in the DC-DC converter section, leading to intermittent power resets; corrosion on RJ-45 connectors in high-humidity environments; and firmware corruption during unexpected power cycles—especially since the module lacks battery-backed memory and relies on flash storage that degrades over write cycles.
A key design vulnerability is its dependence on stable +24V DC from the I/O pack; voltage sags or noise can cause communication timeouts that mimic hardware failure. Additionally, the module’s embedded Linux OS is no longer patched for security vulnerabilities, posing a cyber-risk in modern OT networks.
For maintenance teams, proactive actions include: inspecting Ethernet port integrity for bent pins or oxidation, verifying stable backplane voltage under load, and maintaining offline backups of the module’s configuration file (.xml). Avoid hot-swapping unless explicitly permitted by site procedures, as improper handling can damage the FPGA-based communication controller.

GE IS220UCSAH1A
Lifecycle Status and Migration Strategy
GE has officially discontinued the IS220UCSAH1A as part of the broader Mark VIe product line rationalization. No direct replacement exists within the same form factor, and new production units are unavailable. Continued use carries escalating risks: dwindling verified inventory, lack of factory repair services, and increasing difficulty in sourcing functionally tested units.
As an interim measure, facilities should secure at least one tested spare unit and consider board-level refurbishment by specialized third parties who can replace aging capacitors and reflash firmware. For long-term sustainability, GE recommends migrating to the Mark VIeS platform, where communication functions are integrated into the new IONet architecture via the IS215UCSAH2A or successor modules. This migration requires a full system upgrade—including new I/O packs, controllers, and engineering re-commissioning—but eliminates single-point obsolescence risks and enhances cybersecurity posture through modern TLS/OPC UA support. Until then, rigorous spares management and failure-mode monitoring are essential to avoid unplanned outages.




 Tel:
Tel:  Email:
Email:  WhatsApp:
WhatsApp: