Description
Key Technical Specifications (For Spare Parts Verification)
- Product Model: DS200LPPAG1AAA
- Manufacturer: General Electric (GE Power / GE Vernova)
- System Family: Mark V Turbine Control System
- Functional Type: Low-Level Processor Analog Gateway (LPPA) board
- GE Part Number: DS200LPPAG1AAA
- Input Channels: Multiple analog inputs (typically 4–8 per board), supporting 4–20 mA and ±10 V signals
- Signal Conditioning: Built-in filtering, isolation, and linearization for thermocouples, RTDs, and transmitters
- Backplane Interface: Connects to Mark V core rack via VME-style backplane (DS200 series architecture)
- Diagnostic Capability: Basic self-test on power-up; fault indication via front-panel LEDs
- Firmware Dependency: Fixed logic; tied to specific Mark V application code version
- Form Factor: Standard DS200-series PCB (approx. 9″ x 6″), mounted in turbine control cabinet
System Role and Downtime Impact
Reliability Analysis and Common Failure Modes
The DS200LPPAG1AAA is prone to several age-related failure mechanisms typical of early-1990s industrial electronics. The most common issues include drift or failure in precision operational amplifiers used for signal scaling, degradation of isolation barriers (leading to ground loops or noise coupling), and corrosion of terminal block connectors due to humidity or chemical exposure in turbine enclosures. Electrolytic capacitors on the local DC-DC converter sections often dry out after 15–20 years, causing intermittent resets or erratic readings. Additionally, the board lacks conformal coating in many production batches, making it vulnerable to conductive dust and moisture ingress—especially in coastal or high-humidity sites. As a preventive measure, maintenance teams should perform annual calibration checks against known references, inspect for capacitor bulging or discoloration, clean connector contacts with contact enhancer, and monitor diagnostic logs for repeated “bad value” flags on associated tags. Keeping powered spare boards in a test rack can help detect latent faults before installation.
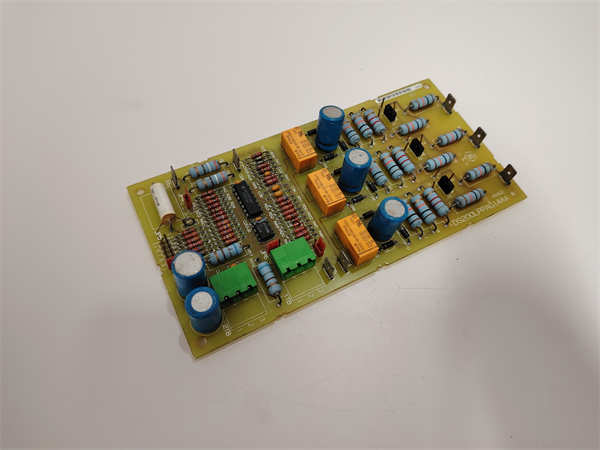
DS200LPPAG1AAA GE


 Tel:
Tel:  Email:
Email:  WhatsApp:
WhatsApp: