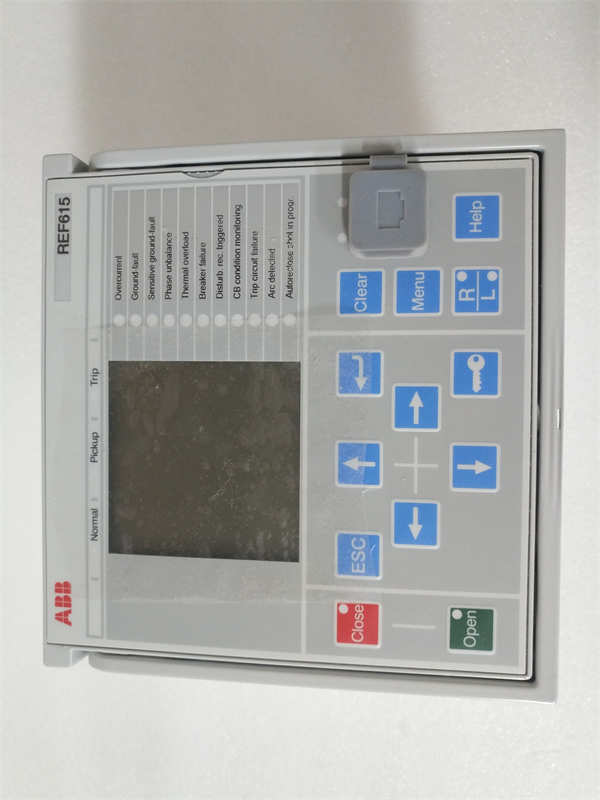
Description
Key Technical Specifications (For Spare Part Verification)
- Product Model: REF615A_1G
- Configuration Code: HAFNAEFCBGC1BQK11G
- Manufacturer: ABB
- Product Family: Relion® REF615 (first generation)
- Input Ratings: 5 A phase CT inputs; 110/115 V phase-to-phase VT inputs
- Protection Functions: 50/51, 50N/51N, 27, 59, 49, 50BF, 79 (depending on firmware C1 variant)
- Communication Interfaces: Ethernet (IEC 61850-8-1 MMS & GOOSE), RS-485 (Modbus RTU or SPA bus), optional IRIG-B time input
- Mounting: Flush-mounted, 4U height panel
- Power Supply: 24–250 V DC/AC (universal)
- Diagnostics: Front-panel LCD with local HMI, LED indicators for trip, alarm, and communication status
System Role and Downtime Impact
The REF615A_1G serves as a primary protection and automation node in medium-voltage switchgear panels across industrial plants, utilities, and infrastructure sites. It is typically installed on outgoing feeders, motor circuits, or transformer secondaries. Its role extends beyond fault clearing—it enables remote monitoring, sequence-of-event recording, and fast interlocking via GOOSE messaging in IEC 61850 architectures.
If this relay fails or loses communication, the immediate consequences include loss of selective tripping during faults, inability to verify breaker position or load status, and potential escalation of minor faults into major outages. In systems without redundant protection, a failed REF615A_1G may force de-energization of the entire feeder until replacement is installed and re-commissioned—leading to production stoppages or safety system degradation.
Reliability Analysis and Common Failure Modes
Despite robust construction, units in service beyond 10–15 years exhibit predictable aging issues:
Electrolytic capacitors in the internal power supply degrade over time, causing intermittent resets or “Power Fail” alarms under load. The Ethernet physical layer (PHY) chip is susceptible to ESD or ground loop damage, resulting in loss of IEC 61850 communication while the relay appears powered. Flash memory wear can corrupt protection settings or prevent configuration uploads via PCM600. Additionally, the front-panel LCD often suffers from contrast fade or dead segments, impairing local operation during network outages.
Design weaknesses include reliance on non-replaceable internal batteries for clock retention in some firmware versions and limited surge immunity on communication ports if external shielding is inadequate.
Preventive maintenance should focus on annual verification of trip logic using secondary injection testing, inspection of terminal tightness and grounding, backup of CID files and settings via compatible PCM600 v2.x software, and visual checks for capacitor bulging or discoloration inside the housing during cabinet access.
Lifecycle Status and Migration Strategy
ABB officially discontinued the first-generation REF615A platform, including the _1G variant, with successor products like the REF615 V2 and now the REF650 in the Relion 650 series. Hitachi Energy provides only limited support for legacy units, with no security patches or compatibility guarantees for modern engineering tools.
Short-term risk mitigation includes securing tested spares with matching configuration codes, performing full functional backups, and engaging specialized third-party services for board-level repair or firmware recovery.
The recommended migration path is upgrading to the REF650, which retains mechanical compatibility with existing cutouts and reuses CT/VT wiring. The new relay supports enhanced cybersecurity (IEC 62443), native OPC UA, and improved arc-flash detection. Migration requires re-engineering in PCM600 v3+ or the Relion Product Suite, but protection logic can often be auto-converted. Facilities should initiate this transition within 12–24 months to maintain regulatory compliance, operational safety, and long-term supportability.




 Tel:
Tel:  Email:
Email:  WhatsApp:
WhatsApp: