Description
Technical Specifications (For Spare Parts Verification)
- Product Model: LTC391AE01
- ABB Order Code: HIEE401782R0001
- Manufacturer: ABB
- System Family: AC800M (part of Extended Automation System 800xA)
- Module Type: Analog input termination unit (used with CI854/CI864 communication interfaces)
- Channel Count: 8 differential inputs
- Supported Signals: 0–20 mA, 4–20 mA, 0–10 V (configurable via jumpers)
- Isolation: Galvanic isolation between field and system side (tested to 500 V AC)
- Connection Type: Screw terminals on removable connector blocks (Type TB854A)
- Diagnostic Features: Open-circuit detection per channel, LED status indicators
- Operating Temperature: 0°C to +55°C
- Mounting: DIN rail in S800 I/O subrack
System Role and Downtime Impact
The ABB LTC391AE01 serves as the physical interface between field instruments (such as transmitters and sensors) and the AC800M controller in legacy 800xA systems. It resides in remote I/O cabinets, typically in hazardous or electrically noisy areas, and conditions analog signals before they are digitized by the associated I/O module (e.g., AI810). While not a logic solver itself, its failure directly compromises the integrity of up to eight critical process variables. Loss of temperature or pressure feedback in a reactor, boiler, or compressor can force operators into manual mode or trigger interlocks, potentially leading to partial or full process shutdown. In safety-related loops, degraded signal quality may also affect SIL compliance.
Reliability Analysis and Common Failure Modes
Although designed for industrial use, the LTC391AE01 is susceptible to long-term environmental stress. The most common failure points are the screw terminal blocks and internal signal conditioning circuitry. Corrosion from humidity or chemical exposure—especially in offshore or chemical plants—can increase contact resistance, causing signal drift or intermittent loss. Additionally, repeated thermal cycling accelerates aging of precision resistors and operational amplifiers in the input stage, leading to calibration drift outside acceptable tolerances.
A notable design limitation is the lack of hot-swap capability; replacement requires de-energizing the I/O subrack, which may impact other modules. The module also depends on proper grounding of the shielded field cables—if improperly terminated, ground loops can induce noise or damage input channels over time. For maintenance teams, recommended practices include: annual inspection of terminal tightness and corrosion, verification of signal accuracy during plant turnarounds using calibrated sources, and keeping spare connector blocks on hand. Storing replacement modules in dry, temperature-controlled environments prevents moisture absorption in PCB materials.
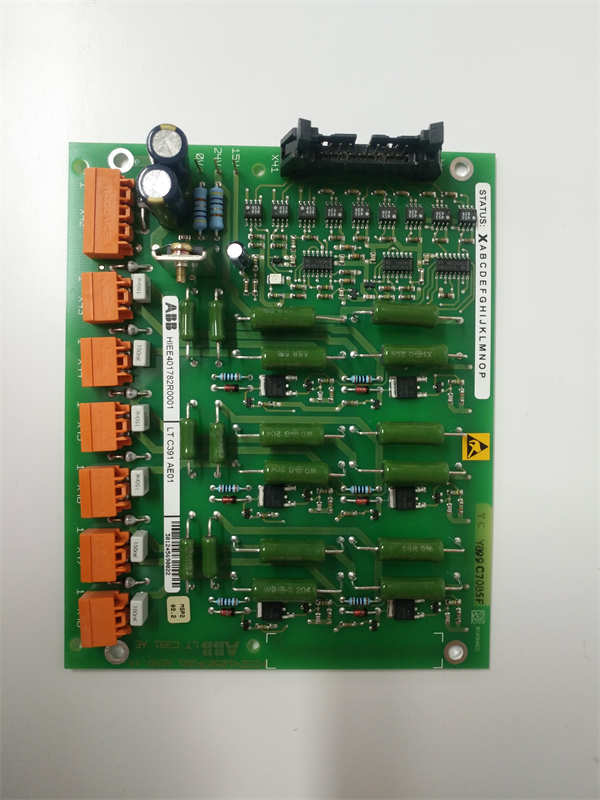
ABB LTC391AE01 HIEE401782R0001
Lifecycle Status and Migration Strategy
ABB has formally discontinued the LTC391AE01 as part of the broader phase-out of the S800 I/O generation. No new production exists, and official repair services are no longer available. Continued reliance on this module poses increasing risk: genuine spares are scarce, counterfeit units have entered secondary markets, and compatibility issues may arise with newer 800xA software versions.
As an interim measure, some users extend system life through careful inventory management, third-party testing of used modules, or localized board-level repairs. However, these approaches carry uncertainty in long-term reliability.
ABB’s official migration path involves upgrading to the newer S800 I/O platform with modules like the TU854 termination unit paired with AI880 analog input cards, or transitioning to the compact AC500-S safety PLC for smaller applications. This modernization requires re-engineering of I/O wiring (due to different terminal layouts), updating control application logic, and re-commissioning. While requiring upfront investment, migration restores access to technical support, improves diagnostic granularity, and ensures compatibility with current cybersecurity and asset management standards—making it the only viable strategy for sustainable operation beyond the next 3–5 years.


 Tel:
Tel:  Email:
Email:  WhatsApp:
WhatsApp: