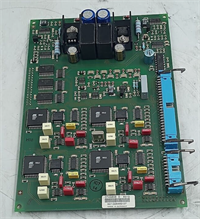
Description
Key Technical Specifications (For Spare Parts Verification)
- Product Model: DSDO115A
- Order Code: 3BSE018298R1
- Manufacturer: ABB (Process Automation, now Hitachi Energy)
- System Platform: AC 800M Controller (used in Symphony Plus, Melody, and custom DCS/PLC systems)
- Output Type: 32 Form A (normally open) relay contacts
- Contact Rating: 2 A at 250 VAC / 30 VDC (resistive load)
- Electrical Isolation: Reinforced insulation between logic and field sides (per IEC 61131-2)
- Module Current Draw: Approx. 700 mA from backplane (+24 VDC)
- Diagnostic Features: Group-level fault indication via front-panel LED; channel status accessible via Control Builder M
- Mounting: DIN rail in I/O cabinet with standard S800 I/O baseplate
- Operating Temperature: 0°C to +60°C
System Role and Downtime Impact
The DSDO115A serves as a critical actuation interface in ABB AC 800M-based control systems widely deployed in power generation, oil & gas, and heavy industry. It translates logical commands from the controller into physical switching actions—energizing pumps, opening dampers, triggering alarms, or enabling safety interlocks. Because a single module controls up to 32 field devices, its failure can cascade into widespread process disruption. For example, in a combined-cycle power plant, loss of DSDO115A functionality could simultaneously disable boiler feedwater pumps, cooling fans, and emission control valves, forcing an immediate turbine trip. Unlike solid-state outputs, relay-based modules like the DSDO115A are subject to mechanical wear, making them more prone to age-related failure in high-cycle applications.
Reliability Analysis and Common Failure Modes
Despite robust industrial design, the DSDO115A exhibits predictable failure patterns after 10–15 years of service:
- Relay contact welding or erosion: Frequent switching under inductive loads (e.g., motor coils) causes arcing, leading to welded contacts (fail-safe closed) or high-resistance opens (fail-dangerous open). This is the most common failure mode.
- Coil driver circuit degradation: The semiconductor drivers that energize relay coils can fail due to thermal stress or voltage transients, causing entire channel banks to become unresponsive.
- Backplane connector corrosion: Moisture ingress in non-climate-controlled cabinets leads to oxidation on the DIN connector pins, resulting in intermittent communication or power loss.
- Capacitor aging on power supply section: Onboard filtering capacitors degrade over time, causing voltage ripple that may trigger false diagnostics or reset behavior.
Recommended maintenance practices include:
- Performing annual contact resistance measurements during outages using a milliohm meter.
- Avoiding inductive loads without snubber circuits to reduce arcing.
- Ensuring cabinet humidity remains below 60% RH with active desiccant or climate control.
- Keeping spare modules powered periodically to prevent electrolytic capacitor drying.
DSDO115A 3BSE018298R1 ABB
Lifecycle Status and Migration Strategy
ABB (Hitachi Energy) has formally obsoleted the DSDO115A as part of its product rationalization toward the AC 900F and newer AC 800M hardware revisions. No new production exists, and official repair services are discontinued. Continued use introduces operational risk due to shrinking spare availability and rising costs in the gray market.
Interim mitigation strategies:
- Source only from suppliers who perform full functional validation—including contact resistance, coil activation, and diagnostic reporting—under simulated load conditions.
- Maintain a minimum of two tested spares per critical system.
- Consider external relay marshalling panels with modern solid-state drivers to offload high-cycle outputs from legacy modules.
Long-term migration path:
Hitachi Energy recommends upgrading to the newer DSDO116A (3BSE048716R1), which offers identical form/fit/function but with improved relay technology and extended lifecycle support. This is a near drop-in replacement requiring:
- Same S800 baseplate and wiring.
- Minor update to I/O configuration in Control Builder M (module type change).
- No re-engineering of field wiring or logic application.
For facilities planning broader modernization, migration to the AC 900F platform or integration with third-party I/O via Modbus TCP/OPC UA gateways may be considered. However, for most users, replacing failed DSDO115A units with verified DSDO116A modules provides the most cost-effective path to restore reliability while deferring full system overhaul.


 Tel:
Tel:  Email:
Email:  WhatsApp:
WhatsApp: