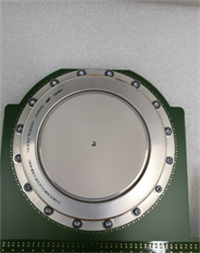
Description
Key Technical Specifications (For Spare Part Verification)
Product Model: 5SHY4045L0006 / 3BHB030310R0001
Manufacturer: ABB
Associated System: ACS 6000 and other high-power AC drive platforms.
IGBT Configuration: Dual IGBT module.
Voltage Rating: Typically 3300V or higher class.
Current Rating: High current capacity (specific amp rating varies by module variant).
Package Type: Press-pack or similar high-power module housing.
Mounting Interface: Specific busbar and heatsink interface design.
Thermal Design: Requires precise cooling system integration and thermal compound application.
Compatible Drive Frame: Specific to particular drive cabinet size and voltage class.
System Positioning & Downtime Impact
This IGBT module is a critical power component within the main inverter section of high-power ABB industrial drives, such as the ACS 6000 series. Its position is directly on the DC bus, switching high voltage and current to synthesize the AC output waveform for large motors. A failure of this module is catastrophic at the device level, typically causing a hard fault that shuts down the entire drive. This leads to an immediate and complete stoppage of the connected process machinery—such as a main blower fan, conveyor, or pump—resulting in significant production losses, potential damage to other drive components (fuses, snubbers), and demanding extensive, skilled labor for replacement and system recommissioning.
Reliability Analysis & Common Failure Points
Common Failure Modes: The predominant failure mechanisms are thermal and electrical overstress. These include bond wire lift-off or fatigue due to thermal cycling, solder joint degradation between substrates and baseplates, and insulation breakdown within the module stack. Gate driver faults or voltage transients can also cause destructive short-circuit failures (shoot-through). Contamination or improper application of thermal interface material leading to localized overheating is another frequent cause.
Inherent Vulnerabilities: As a high-power semiconductor, this module is intrinsically vulnerable to voltage spikes on the supply side, excessive dv/dt or di/dt stresses, and inadequate cooling. Its operational lifespan is directly tied to thermal management efficacy and the electrical “cleanliness” of the installation. Earlier generation IGBTs, like this one, may have less robust short-circuit withstand capability compared to modern counterparts.
Preventive Maintenance Recommendations: Maintenance focus must be on the module’s operating environment. Regularly monitor and record heatsink temperature trends. Ensure cooling water quality and flow rates are within specification for liquid-cooled systems. Inspect and maintain the integrity of the thermal grease/pads during scheduled downtime. Perform thorough inspections of DC bus capacitors and snubber circuits, as their failure can precipitate IGBT damage. Use power quality analyzers to check for line-side harmonics and transients that stress the module.
Lifecycle & Migration Strategy
Official Status & Risk: ABB has officially discontinued production of this specific IGBT module generation. The primary risk is supply chain failure: sourcing genuine, functional spares is increasingly difficult, expensive, and time-consuming. Relying on unknown surplus or refurbished units introduces significant reliability and safety risks into a critical asset. Furthermore, technical support and detailed application notes for this legacy component are no longer available.
Interim Mitigation Solutions: To temporarily sustain operations, plants may establish a strategic spare part inventory from reputable surplus channels, though this carries cost and authenticity risks. Another option is engaging specialized third-party services for IGBT module repair or refurbishment. It is critical to test any spare or repaired module thoroughly before installation. These are temporary measures that do not address the systemic obsolescence risk.
Migration/Replacement Pathway: The definitive long-term strategy is a platform upgrade. ABB’s official migration path is to replace the entire drive cabinet or power stack with a modern equivalent, such as an ACS6080 or other contemporary drive model. This modernizes the entire power conversion system, offering improved efficiency, diagnostics, and reliability. A less extensive, though still major, retrofit involves replacing the obsolete IGBT stack with a newer generation power semiconductor module and its associated gate drivers within the existing frame, which requires significant engineering by ABB or a certified partner. Both paths necessitate careful planning for motor compatibility, control system interfacing, and downtime scheduling.



 Tel:
Tel:  Email:
Email:  WhatsApp:
WhatsApp: