Description
Key Technical Specifications (For Spare Parts Verification)
- Product Model: 216EA61B
- Manufacturer: ABB
- System Family: AC800F / Freelance Distributed Control System (DCS)
- Module Type: Foundation Fieldbus H1 Communication Interface
- Mounting: DIN rail, compatible with AC800F chassis
- Communication Protocol: IEC 61158 Type 1 (Foundation Fieldbus H1)
- Data Rate: 31.25 kbit/s
- Power Supply: Backplane-powered (+5 V, +24 V) from AC800F rack
- Physical Interface: Dedicated terminal block; supports redundant FF-H1 segments when deployed in pairs
- Firmware Compatibility: Freelance 2013 and earlier versions (project-dependent)
System Role and Downtime Impact
The ABB 216EA61B functions as the primary Fieldbus gateway linking the AC800F controller to smart field devices on a Foundation Fieldbus segment. It is commonly deployed in critical process areas such as chemical reactors, distillation units, or utility systems where multiple instruments share a single digital bus. In non-redundant configurations, failure of this module results in complete loss of communication with all connected Fieldbus devices on that segment. This causes immediate disruption of measurement and control signals, often triggering safety interlocks or forcing manual operation. In continuous production environments, such an event typically leads to full-line shutdowns, material loss, and extended recovery time until a verified replacement is installed and recommissioned.
Reliability Analysis and Common Failure Modes
Despite its industrial-grade design, the 216EA61B exhibits age-related vulnerabilities typical of legacy electronics. The most prevalent failure mechanism involves degradation of onboard electrolytic capacitors, leading to unstable power regulation, intermittent communication errors, or total module lockup. Additionally, the Fieldbus transceiver circuitry is susceptible to voltage surges induced through field cabling—especially in facilities lacking proper grounding or surge protection—resulting in damaged communication ports. A known design limitation is its dependence on volatile memory for configuration retention during brief power interruptions; without stable system power or a battery-backed controller, parameter loss may occur after outages. For preventive maintenance, technicians should routinely inspect for bulging or leaking capacitors, verify terminal tightness to prevent arcing, clean dust from ventilation paths, and monitor diagnostic LEDs for early signs of communication faults. Regular backup of Fieldbus Device Descriptions (DDs) and segment configurations is also strongly advised to accelerate recovery.
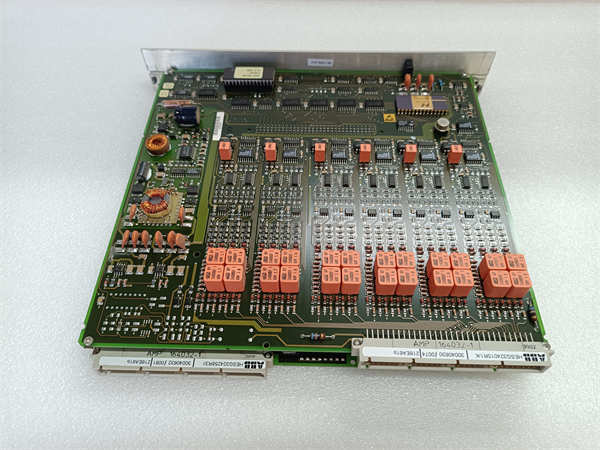

ABB 216EA61b
Lifecycle Status and Migration Strategy
ABB has officially discontinued the 216EA61B as part of the broader end-of-life phase-out of the AC800F platform, with formal obsolescence notices issued in the late 2010s. Continued operation entails significant risks: no new units are available from ABB, third-party inventory is scarce and often untested, and engineering support for diagnostics or troubleshooting is extremely limited. As a short-term mitigation, facilities may source tested-used modules from specialized surplus vendors or pursue board-level repairs, though reliability cannot be guaranteed. The recommended long-term solution is migration to ABB’s current distributed control platform, System 800xA with AC 800M controllers. This path typically requires replacing the entire I/O infrastructure—including Fieldbus interfaces (e.g., with modern CI854A or redundant FF modules compatible with AC 800M)—and re-engineering control logic in Control Builder M. While capital-intensive, such a migration restores access to up-to-date cybersecurity features, ongoing vendor support, and sustainable spare parts availability, ultimately reducing operational and business continuity risk.


 Tel:
Tel:  Email:
Email:  WhatsApp:
WhatsApp: 



